Anxiety is a common mental health condition that can manifest in various physical symptoms, including chest pain. The experience of chest pain during anxiety can be distressing and may lead to concerns about heart health. In this article, we will explore the relationship between anxiety and chest pain, discussing the causes, symptoms, and management strategies. Whether you’re wondering if anxiety can cause chest pain or seeking guidance on managing anxiety-related chest discomfort, this article aims to provide valuable insights.
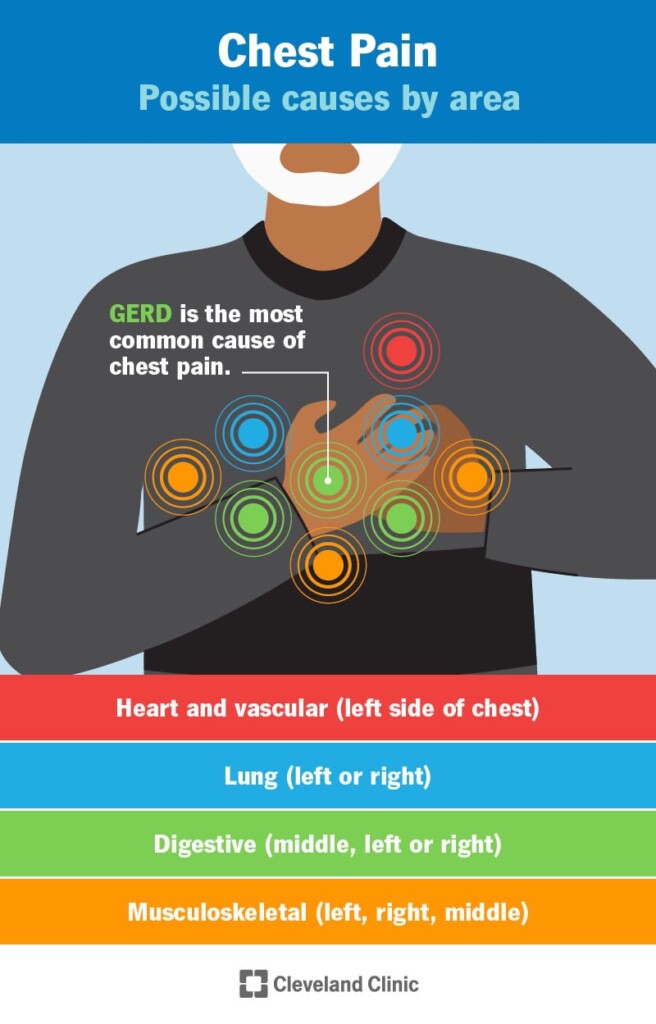
Understanding Anxiety-Induced Chest Pain: Anxiety-induced chest pain refers to discomfort or tightness in the chest that occurs during or as a result of an anxiety episode. While anxiety itself does not directly damage the heart, it can cause physical sensations due to the body’s stress response. These sensations may include chest pain, pressure, or a feeling of tightness.
Causes and Mechanisms: Several factors contribute to anxiety-induced chest pain. During periods of anxiety or panic, the body experiences increased stress hormones, muscle tension, and changes in heart rate. These physiological responses can trigger chest pain or discomfort. Additionally, anxiety-related hyperventilation, where breathing becomes rapid and shallow, can lead to chest sensations.
Symptoms of Anxiety-Induced Chest Pain: Anxiety-induced chest pain can manifest differently for each individual. Common symptoms include a dull or sharp pain in the chest, a squeezing sensation, tightness, or pressure. It is important to note that chest pain should always be evaluated by a healthcare professional to rule out any underlying medical conditions.
Managing Anxiety-Related Chest Discomfort: If you experience anxiety-induced chest pain, it is essential to address both the underlying anxiety and the physical symptoms. Here are some management strategies:
- Seek Professional Guidance: Consult with a healthcare professional, such as a primary care physician or mental health specialist, to evaluate your symptoms, rule out any underlying medical conditions, and develop an appropriate management plan.
- Practice Stress-Reduction Techniques: Engage in stress-reducing activities like deep breathing exercises, meditation, yoga, or progressive muscle relaxation. These techniques can help calm the body and alleviate anxiety symptoms, including chest discomfort.
- Cognitive-Behavioral Therapy (CBT): Consider seeking therapy, such as CBT, which focuses on identifying and challenging negative thought patterns associated with anxiety. CBT can help reframe anxious thoughts and develop coping strategies to manage anxiety-related symptoms.
- Lifestyle Modifications: Adopt a healthy lifestyle by prioritizing regular exercise, maintaining a balanced diet, getting adequate sleep, and avoiding substances that may exacerbate anxiety symptoms, such as caffeine or alcohol.
- Medication Management: In some cases, medication may be prescribed to help manage anxiety symptoms. Consult with a healthcare professional to determine if medication is an appropriate option for you.
Anxiety-induced chest pain can be distressing, but it is important to understand that anxiety is the underlying cause and not a direct threat to your heart. If you experience chest pain or discomfort, it is essential to consult with a healthcare professional to rule out any underlying medical conditions. By addressing the root cause of anxiety and adopting appropriate management strategies, you can effectively manage anxiety-related chest discomfort and improve your overall well-being. Remember, seeking professional guidance and support is crucial in managing anxiety and its associated symptoms.
As an Amazon Associate we earn from qualifying purchases through some links in our articles.