Understanding the Connection
Have you ever experienced a sudden bout of dizziness, paired with a throbbing headache, neck pain, overwhelming fatigue, and a general sense of weakness? It’s a cocktail of symptoms that can leave anyone feeling bewildered and worried. While these symptoms might seem unrelated at first glance, they can often be traced back to an unsuspecting culprit: stomach issues.
Many people overlook the digestive system when pinpointing the cause of such discomforts. However, the gut and brain are intricately connected, with problems in the stomach potentially leading to a cascade of other symptoms. Understanding this connection is crucial for identifying the underlying issue and finding effective relief.
In this article, we will explore various stomach-related problems that can cause sudden dizziness, headaches, neck pain, weakness, tiredness, and fatigue. From common conditions like GERD and gastritis to more complex issues such as IBS and celiac disease, we’ll delve into how these ailments can disrupt your entire system. By recognizing these links, you can better understand your symptoms and take steps toward addressing them.

How Can GERD Lead to Dizziness and Fatigue?
Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease (GERD) is a common condition that occurs when stomach acid frequently flows back into the esophagus, irritating its lining. This acid reflux can lead to a host of uncomfortable symptoms, some of which might surprise you.
Symptoms and Causes of GERD
GERD’s primary symptoms include heartburn, regurgitation, and difficulty swallowing. However, the effects of GERD can extend beyond the digestive system, causing issues such as:
- Dizziness: When the vagus nerve, which runs from the brain to the abdomen, is irritated by acid reflux, it can lead to dizziness. This nerve plays a crucial role in controlling heart rate, digestion, and reflexes like coughing, making its irritation particularly impactful.
- Headache and Neck Pain: The discomfort and stress caused by chronic acid reflux can manifest as tension headaches and neck pain. Stress often triggers muscle tension, which can lead to headaches and pain in the neck area.
- Weakness and Fatigue: GERD can disrupt sleep due to nighttime acid reflux, leading to chronic fatigue. Additionally, the constant discomfort and pain can wear down your energy levels over time.
The symptoms of GERD can be exacerbated by certain medications, including common pain relievers. For a personal account of how medications can affect the stomach, check out Can Ibuprofen Cause Stomach Aches and Diarrhea? My Personal Struggle.

Managing GERD to Alleviate Symptoms
Effectively managing GERD can help alleviate its wide-ranging symptoms. Here are some tips:
- Dietary Changes: Avoid trigger foods such as spicy dishes, caffeine, and chocolate. Eating smaller, more frequent meals can also help reduce reflux.
- Lifestyle Adjustments: Elevate the head of your bed to prevent nighttime reflux, avoid lying down immediately after meals, and maintain a healthy weight.
- Medications: Over-the-counter antacids, H2 blockers, or proton pump inhibitors can help manage acid production. For a reliable option, consider HealthCareAisle Omeprazole 20 mg, 42 Delayed-Release Capsules – Acid Reducer, Treats Frequent Heartburn. Taking this once per day for a month can help you start feeling better if your issue is acid-related. Remember, it’s more of a preventative measure, so consistency is key.
Understanding the broader impacts of GERD on your body can help you take more comprehensive steps to manage it, reducing not just digestive discomfort but also related symptoms like dizziness and fatigue.
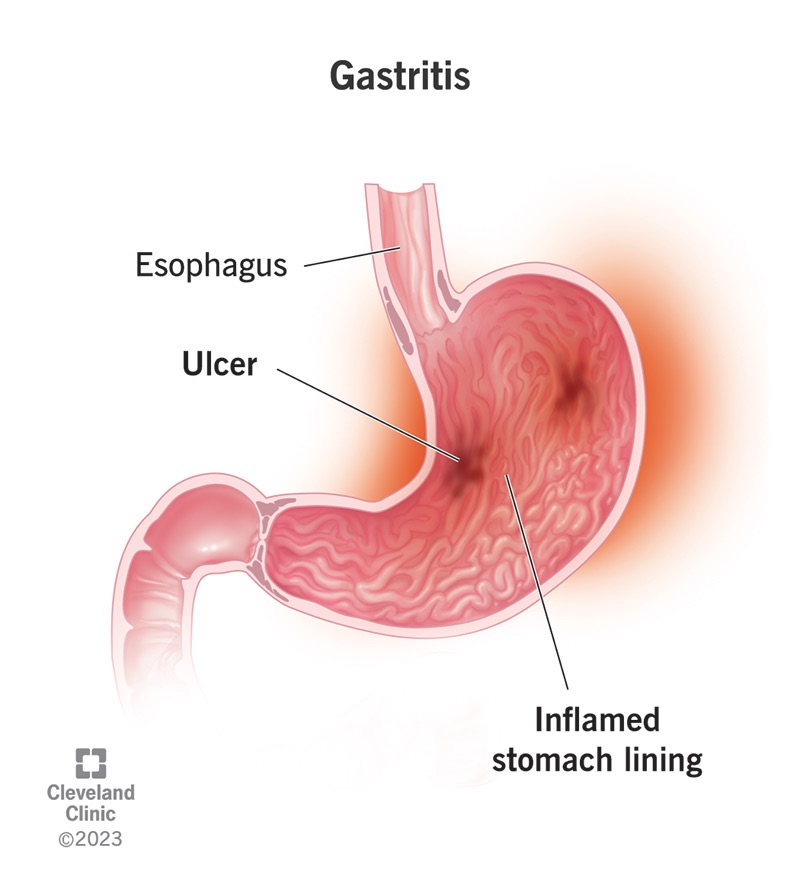
Gastritis: An Inflammation with Far-Reaching Effects
Gastritis is another common stomach issue that can wreak havoc on your overall well-being. It’s characterized by inflammation of the stomach lining, which can lead to a variety of symptoms that extend beyond your gut.
Symptoms and Causes of Gastritis
Gastritis can be caused by several factors, including excessive alcohol consumption, prolonged use of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), stress, and infections like H. pylori. The symptoms of gastritis can include:
- Dizziness: The inflammation and pain associated with gastritis can trigger dizziness, especially when the condition becomes chronic.
- Headache and Neck Pain: Chronic gastritis can lead to stress and tension, contributing to headaches and neck pain.
- Weakness and Fatigue: The persistent discomfort and pain from gastritis can drain your energy, leaving you feeling weak and fatigued.
For immediate relief of gastritis symptoms, an effective antacid can be a lifesaver. Consider using Mylanta Antacid and Gas Relief, Maximum Strength Formula, Classic Flavor. This product can help soothe your stomach and reduce symptoms like heartburn and gas.
Managing Gastritis to Improve Overall Health
Managing gastritis effectively can significantly improve your overall health and reduce related symptoms. Here are some tips:
- Dietary Adjustments: Avoid foods and drinks that can irritate your stomach lining, such as spicy foods, alcohol, and caffeine. Opt for a bland diet when symptoms flare up.
- Stress Management: Incorporate stress-reducing techniques like meditation, yoga, or regular exercise into your daily routine to help manage gastritis.
- Medications: Use medications like proton pump inhibitors or H2 blockers to reduce stomach acid production. Antacids, like the previously mentioned Mylanta, can provide quick relief from acute symptoms.
By understanding the causes and effects of gastritis, you can take proactive steps to manage it, thereby reducing not only stomach discomfort but also associated symptoms like dizziness, headaches, and fatigue.
Peptic Ulcers and Their Unexpected Symptoms
Peptic ulcers are sores that develop on the lining of the stomach, lower esophagus, or small intestine. They can cause significant discomfort and lead to a range of symptoms that extend beyond the digestive system.
Symptoms and Causes of Peptic Ulcers
Peptic ulcers are primarily caused by an infection with the bacterium H. pylori or prolonged use of NSAIDs. The symptoms can include:
- Dizziness: Chronic blood loss from an ulcer can lead to anemia, which in turn causes dizziness.
- Headache and Neck Pain: The stress and pain from ulcers can contribute to tension headaches and neck pain.
- Weakness and Fatigue: Anemia from chronic bleeding can result in persistent fatigue and weakness.
Managing Peptic Ulcers for Symptom Relief
Effectively managing peptic ulcers is crucial for alleviating their wide-ranging symptoms. Here are some tips:
- Medications: Proton pump inhibitors and antibiotics (if H. pylori is present) are commonly prescribed to treat peptic ulcers. Antacids can also provide symptomatic relief.
- Dietary Changes: Avoid foods that can irritate the stomach lining, such as spicy foods, alcohol, and caffeine. Eating smaller, more frequent meals can help reduce gastric irritation.
- Lifestyle Adjustments: Quit smoking and limit alcohol consumption, as both can exacerbate ulcer symptoms.
For additional relief from ulcer-related symptoms like heartburn and gas, consider using Mylanta Antacid and Gas Relief, Maximum Strength Formula, Classic Flavor. This product can help soothe the stomach and provide quick relief.
Peptic ulcers require proper medical diagnosis and treatment. If you suspect you have an ulcer, consult a healthcare provider for appropriate tests and treatment plans. Understanding the broader impacts of peptic ulcers on your body can help you take comprehensive steps to manage them, reducing not just digestive discomfort but also related symptoms like dizziness and fatigue.
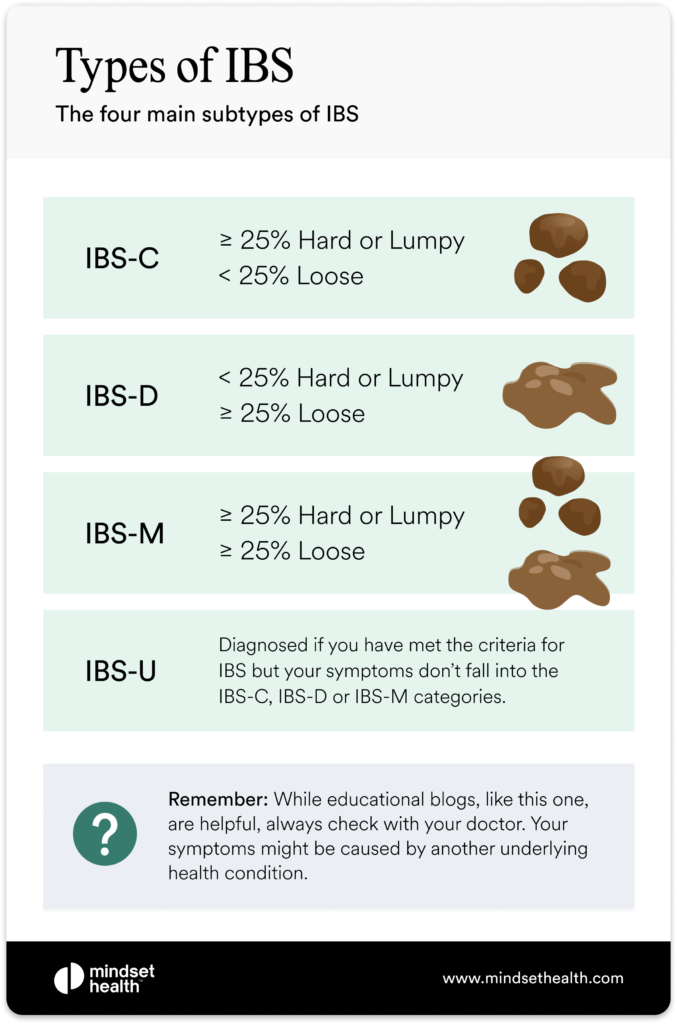
IBS: More Than Just a Stomach Issue
Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS) is a common disorder that affects the large intestine. While it primarily causes digestive symptoms, its impact can be felt throughout the body, leading to issues far beyond the gut.
Symptoms and Causes of IBS
IBS is characterized by a combination of symptoms, including abdominal pain, cramping, bloating, gas, and altered bowel habits (diarrhea, constipation, or both). The exact cause of IBS is unknown, but factors such as diet, stress, and hormonal changes can trigger symptoms. These can also lead to:
- Dizziness: Dehydration from chronic diarrhea can cause dizziness.
- Headache and Neck Pain: Stress and tension from dealing with chronic IBS symptoms can lead to headaches and neck pain.
- Weakness and Fatigue: The persistent discomfort and disruptions in bowel habits can drain your energy, causing weakness and fatigue.
For more insights into managing digestive distress, check out Understanding Persistent Digestive Distress: Unraveling Diarrhea, Nausea, and Stomach Pain.
Managing IBS to Improve Overall Well-Being
Effectively managing IBS can help alleviate its wide-ranging symptoms and improve your quality of life. Here are some tips:
- Dietary Changes: Identify and avoid trigger foods, such as dairy, gluten, and certain high-fiber foods. A low-FODMAP diet can also help reduce symptoms for many people with IBS.
- Stress Management: Incorporate relaxation techniques like meditation, yoga, or deep breathing exercises to help manage stress, which can exacerbate IBS symptoms.
- Medications and Supplements: Over-the-counter options like antispasmodics, fiber supplements, and probiotics can help manage symptoms. In some cases, prescription medications may be necessary.
Understanding that IBS can affect more than just your digestive system is crucial for comprehensive management. By addressing the triggers and symptoms holistically, you can reduce the impact of IBS on your overall health and well-being.
For a personal perspective on managing a chronic condition, explore Having Chronic Stomach Issues: A Personal Health Journey.
The Silent Struggles of Celiac Disease
Celiac disease is an autoimmune disorder in which the ingestion of gluten leads to damage in the small intestine. This condition can cause a wide array of symptoms that extend beyond digestive issues, affecting various aspects of your health.
Symptoms and Causes of Celiac Disease
Celiac disease occurs in genetically predisposed individuals when they consume gluten—a protein found in wheat, barley, and rye. The immune reaction damages the small intestine’s lining, leading to malabsorption of nutrients. Symptoms can vary widely but often include:
- Dizziness: Malnutrition and anemia due to poor nutrient absorption can cause dizziness.
- Headache and Neck Pain: Nutrient deficiencies, particularly in B vitamins and iron, can lead to headaches and associated neck pain.
- Weakness and Fatigue: Chronic malabsorption can result in significant fatigue and general weakness.
For a deeper understanding of how chronic conditions can impact overall health, read about Anxiety: A Personal Journey Beyond Prescription Medication, which explores the broader implications of managing health issues.
Managing Celiac Disease for Better Health
Effectively managing celiac disease involves strict adherence to a gluten-free diet. Here are some tips to help manage the condition:
- Gluten-Free Diet: Completely eliminate gluten from your diet. This includes avoiding foods containing wheat, barley, and rye, as well as being cautious of cross-contamination.
- Nutritional Supplements: Due to malabsorption, it may be necessary to take supplements to correct deficiencies, particularly in iron, calcium, vitamin D, and B vitamins.
- Regular Monitoring: Work closely with a healthcare provider to monitor your nutrient levels and adjust your diet and supplements as needed.
Celiac disease requires lifelong management, but with strict dietary control, you can alleviate symptoms and prevent long-term complications. Understanding the broader impact of celiac disease on your body can help you take comprehensive steps to manage it effectively.
For more on how diet and digestive health can affect overall well-being, check out Burping Up Puke? Here’s What Your Body Is Trying to Tell You.

Food Poisoning: A Common Culprit
Food poisoning is an unpleasant but all-too-common experience that can cause a range of symptoms, from stomach cramps to more widespread effects like dizziness and fatigue. Understanding the causes and symptoms of food poisoning can help you take swift action to manage and prevent it.
Symptoms and Causes of Food Poisoning
Food poisoning occurs when you consume contaminated food or beverages. Bacteria, viruses, parasites, or toxins can cause this contamination. Common culprits include Salmonella, E. coli, and Norovirus. Symptoms typically include:
- Dizziness: Dehydration from vomiting and diarrhea can lead to dizziness.
- Headache and Neck Pain: Fluid loss and the body’s response to infection can cause headaches and associated neck pain.
- Weakness and Fatigue: The body’s effort to fight off the infection and the dehydration that accompanies it can result in significant weakness and fatigue.
For additional insights into managing symptoms like dizziness, refer to Understanding Neck Pain and Dizziness.
Managing Food Poisoning for Symptom Relief
Here are some steps to manage food poisoning effectively and alleviate its symptoms:
- Stay Hydrated: Drink plenty of fluids, such as water, clear broths, and oral rehydration solutions, to prevent dehydration. Avoid caffeine and alcohol, which can exacerbate dehydration.
- Rest: Allow your body to recover by getting plenty of rest. This helps conserve energy and aids in the healing process.
- Eat Light: Once you can tolerate food, start with bland, easy-to-digest foods like bananas, rice, applesauce, and toast (the BRAT diet). Avoid dairy, fatty, and spicy foods until your symptoms improve.
- Medication: Over-the-counter medications like antidiarrheals and anti-nausea drugs can help manage symptoms. However, it’s important to consult with a healthcare provider before taking these, especially if you have severe symptoms.
Food poisoning generally resolves on its own within a few days, but severe cases may require medical attention. If you experience persistent symptoms, high fever, or signs of dehydration, seek medical care immediately.
For a broader perspective on digestive health and its impact on overall well-being, explore Having Chronic Stomach Issues: A Personal Health Journey.
The Impact of Inflammatory Bowel Disease
Inflammatory Bowel Disease (IBD) encompasses conditions such as Crohn’s Disease and Ulcerative Colitis, which involve chronic inflammation of the digestive tract. These conditions can have widespread effects on your health beyond the digestive system.
Symptoms and Causes of IBD
IBD is characterized by long-term inflammation of the gastrointestinal tract, which can cause a variety of symptoms, including:
- Dizziness: Chronic blood loss from IBD can lead to anemia, causing dizziness.
- Headache and Neck Pain: Chronic inflammation and the stress of managing a long-term condition can lead to tension headaches and neck pain.
- Weakness and Fatigue: The persistent inflammation and nutrient malabsorption associated with IBD can result in significant fatigue and weakness.
For more on how chronic digestive conditions can impact your overall health, consider reading Anxiety: A Personal Journey Beyond Prescription Medication, which delves into the broader implications of managing long-term health issues.
Managing IBD to Improve Quality of Life
Effectively managing IBD requires a comprehensive approach, often involving medication, lifestyle changes, and sometimes surgery. Here are some strategies:
- Medications: Anti-inflammatory drugs, immunosuppressants, and biologics are commonly used to control inflammation and manage symptoms. Consult with a gastroenterologist for the best treatment plan.
- Dietary Adjustments: Certain foods can trigger IBD symptoms. Keeping a food diary can help identify and avoid these triggers. A balanced diet that supports overall health and minimizes inflammation is crucial.
- Stress Management: Stress can exacerbate IBD symptoms. Incorporating stress-reduction techniques like yoga, meditation, and regular exercise can be beneficial.
- Regular Monitoring: Regular check-ups with your healthcare provider are essential to monitor disease progression and adjust treatments as needed.
Understanding that IBD affects more than just the digestive system can help you take a holistic approach to managing the condition, thereby improving your overall quality of life.
For additional strategies on managing symptoms like nausea and stomach pain, refer to Understanding Persistent Digestive Distress: Unraveling Diarrhea, Nausea, and Stomach Pain.
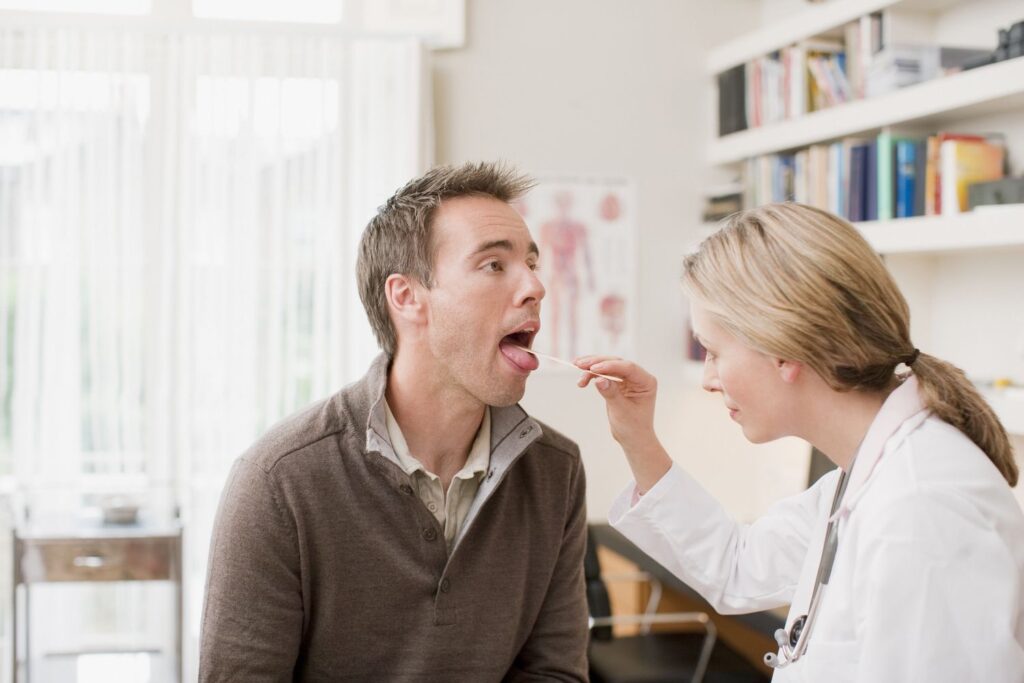

Seeking Medical Help: When to See a Doctor
Experiencing symptoms like sudden dizziness, headaches, neck pain, weakness, tiredness, and fatigue can be distressing. While some of these symptoms may be managed at home, it’s crucial to know when to seek professional medical help to ensure there isn’t a more serious underlying condition.
Signs That You Should See a Doctor
If you experience any of the following, it’s important to consult a healthcare professional:
- Persistent Symptoms: If your symptoms persist for more than a few days or weeks despite home remedies and lifestyle changes, it’s time to see a doctor.
- Severe Pain: Intense abdominal pain, headaches, or neck pain that doesn’t subside with over-the-counter medications should be evaluated by a professional.
- Significant Weight Loss: Unintended weight loss can be a sign of a more serious health issue and should be addressed promptly.
- Blood in Stool or Vomit: This can indicate internal bleeding, which requires immediate medical attention.
- High Fever: A fever above 101°F (38.3°C) accompanying these symptoms could indicate an infection or another serious condition.
- Signs of Dehydration: Dizziness, dry mouth, dark urine, and decreased urine output can be signs of dehydration, which may require medical treatment.
For more insights on when to seek medical advice for stomach issues, check out Having Chronic Stomach Issues: A Personal Health Journey.
Preparing for Your Doctor’s Visit
To make the most of your medical appointment, consider the following tips:
- Keep a Symptom Diary: Track your symptoms, including their frequency, duration, and any potential triggers. This information can help your doctor diagnose your condition more accurately.
- List Medications and Supplements: Provide a list of all medications, supplements, and over-the-counter drugs you are taking, as they can affect your symptoms and treatment options.
- Prepare Questions: Write down any questions or concerns you have about your symptoms and treatment options. This ensures you don’t forget anything important during your visit.
By seeking timely medical help and providing your doctor with detailed information, you can receive a more accurate diagnosis and effective treatment plan. Remember, your health is worth the effort, and professional guidance can make a significant difference.
For additional tips on managing symptoms like dizziness, refer to Understanding Neck Pain and Dizziness.
Connecting the Dots
As someone who had or does suffer from most of the issues in this list, it can be absolutely hell to live with. Understanding the connection between stomach issues and symptoms like dizziness, headaches, neck pain, weakness, tiredness, and fatigue can be crucial for effective treatment and improved well-being. Conditions such as GERD, gastritis, peptic ulcers, IBS, celiac disease, food poisoning, and IBD can have far-reaching effects on your body beyond the digestive system.
Addressing these underlying stomach issues often requires a combination of dietary changes, lifestyle adjustments, and medical treatment. Recognizing the symptoms and knowing when to seek professional help can make a significant difference in managing your health.
Remember, your gut health is deeply intertwined with your overall health. By taking proactive steps to manage stomach issues, you can alleviate a wide range of symptoms and enhance your quality of life. If you’re experiencing persistent or severe symptoms, don’t hesitate to consult a healthcare professional for a thorough evaluation and personalized treatment plan.
For a deeper dive into managing chronic stomach issues and related symptoms, explore Understanding Persistent Digestive Distress: Unraveling Diarrhea, Nausea, and Stomach Pain. Additionally, maintaining a healthy lifestyle and staying informed about your condition can empower you to take control of your health and well-being.
Thank you for joining us on this exploration of the connections between stomach issues and a range of troubling symptoms. We hope this information helps you better understand your health and take meaningful steps towards relief and recovery.
As an Amazon Associate we earn from qualifying purchases through some links in our articles.