Foot gangrene is a severe condition characterized by tissue death in the foot due to inadequate blood supply. It typically occurs as a result of an underlying condition or injury that restricts blood flow, leading to tissue decay. This article provides an overview of foot gangrene, including its causes, symptoms, and available treatment options.
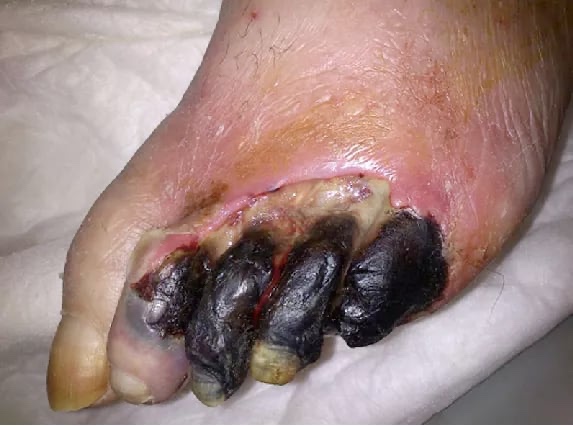
Understanding the Causes
Foot gangrene can have several causes, including:
- Peripheral artery disease (PAD): A condition that narrows or blocks the arteries supplying blood to the feet, usually caused by atherosclerosis.
- Diabetes: High blood sugar levels in individuals with diabetes can damage blood vessels and impair circulation, increasing the risk of foot complications.
- Infection: Infections that are left untreated or not properly managed can lead to tissue damage and gangrene.
- Trauma or injury: Severe injuries or trauma to the foot, such as fractures or crush injuries, can disrupt blood flow and contribute to the development of gangrene.
Recognizing the Symptoms
Common symptoms of foot gangrene may include:
- Discoloration: The affected area may appear pale, bluish, black, or greenish due to the lack of blood supply.
- Pain: Initially, there may be severe pain, which can later turn into numbness as nerve damage progresses.
- Foul odor: Gangrene can cause a noticeable foul smell due to tissue decay and bacterial infection.
- Ulcers or sores: Open sores or ulcers that are slow to heal or do not respond to treatment can be a sign of gangrene.
Seeking Medical Treatment
If foot gangrene is suspected, immediate medical attention is crucial. Treatment options may include:
- Debridement: The removal of dead or infected tissue to promote healing and prevent the spread of infection.
- Antibiotics: Oral or intravenous antibiotics may be prescribed to treat any underlying infection.
- Revascularization: In cases where blood flow is severely compromised, surgical interventions such as bypass surgery or angioplasty may be necessary to restore circulation.
- Amputation: In severe cases where the condition cannot be effectively treated or if there is a risk of systemic infection, amputation of the affected part of the foot or lower limb may be required.
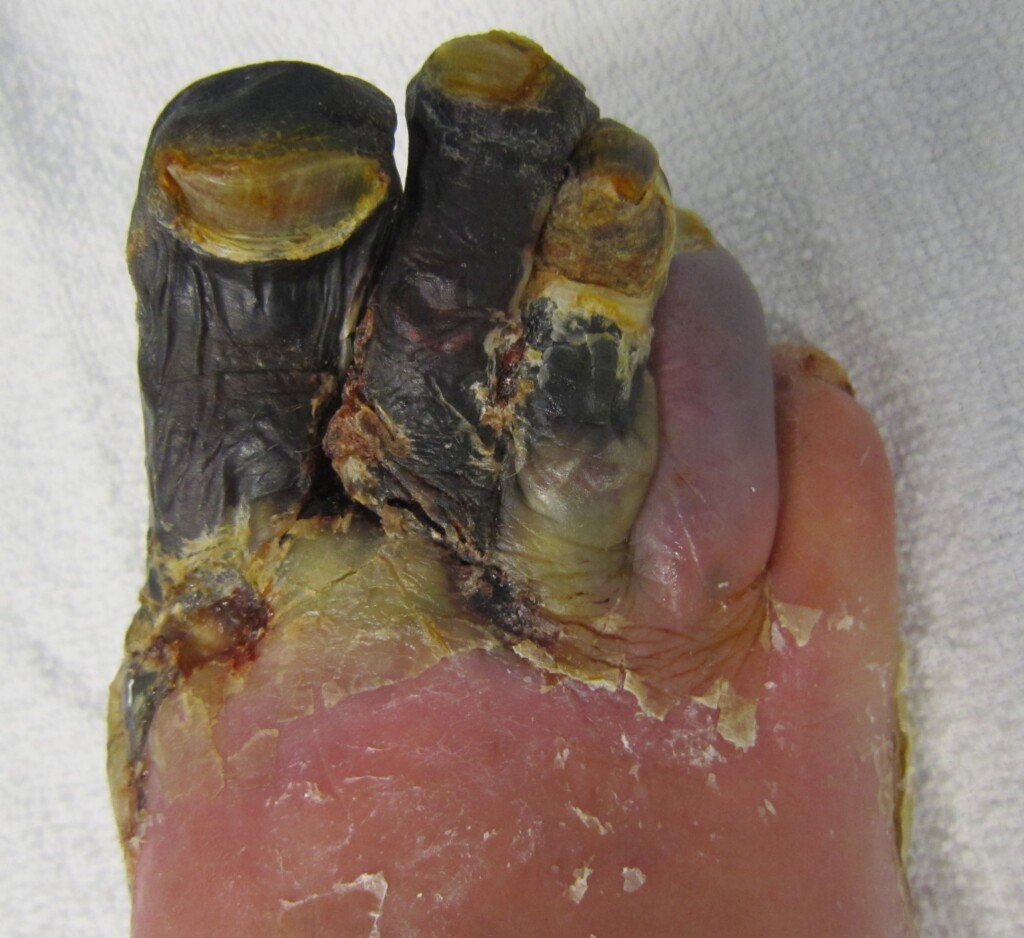
Prevention and Self-Care
Taking steps to prevent foot gangrene is crucial, especially for individuals at higher risk due to diabetes or peripheral artery disease. Some preventive measures include:
- Proper foot care: Regularly inspecting the feet for any signs of injury or infection and practicing good hygiene.
- Managing underlying conditions: Controlling blood sugar levels in diabetes and following a healthy lifestyle to manage peripheral artery disease.
- Avoiding smoking: Smoking can further restrict blood flow and increase the risk of complications.
- Seeking medical attention: Promptly addressing any foot injuries, infections, or concerns to prevent complications.
Foot gangrene is a serious condition characterized by tissue death in the foot due to insufficient blood supply. Understanding its causes, recognizing the symptoms, and seeking immediate medical attention are crucial for effective treatment. By following preventive measures and practicing self-care, individuals can reduce the risk of foot gangrene and related complications.
As an Amazon Associate we earn from qualifying purchases through some links in our articles.




